Main Activities
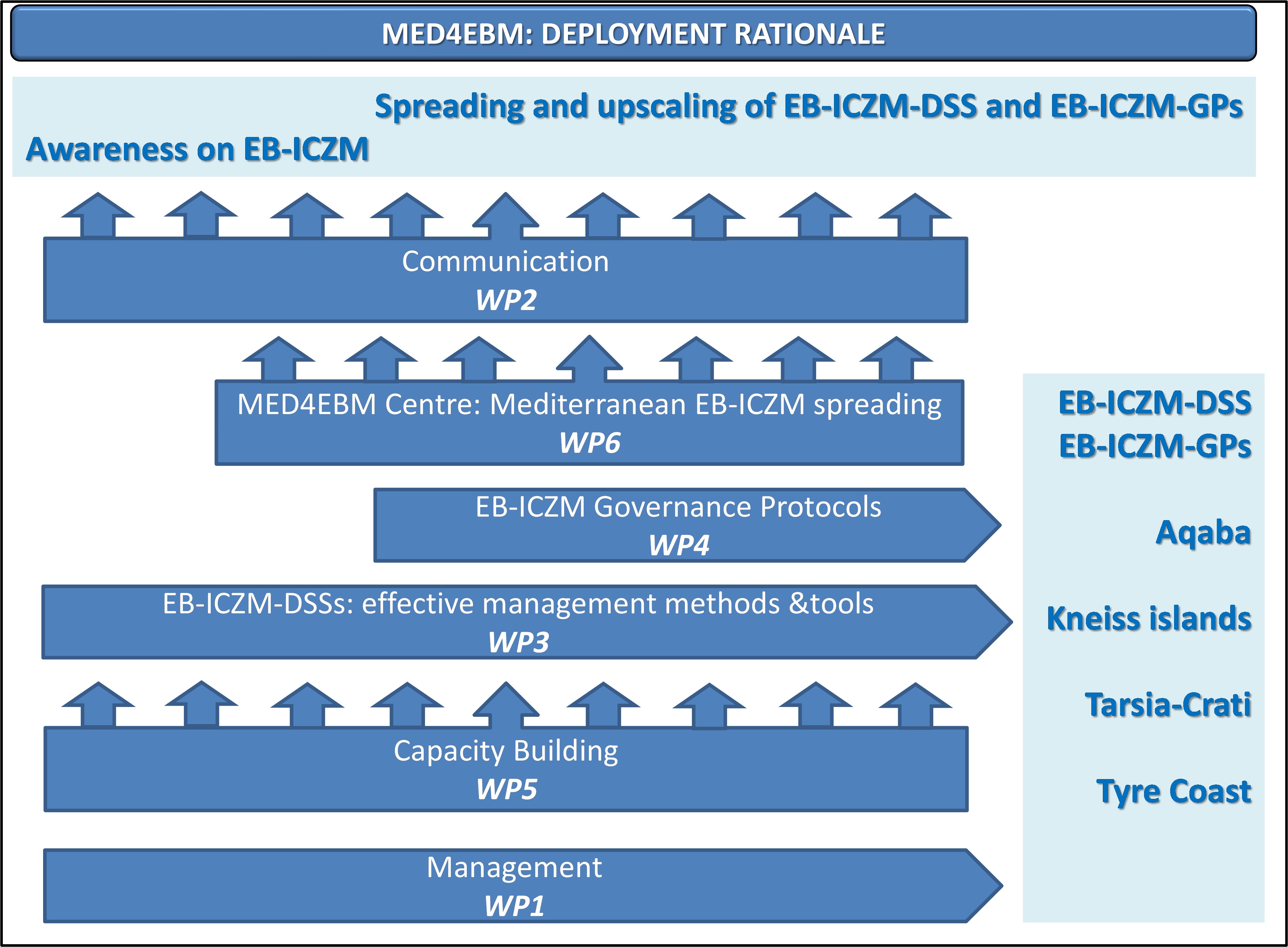
MED4EBM is organized in six Work Packages (WPs), according to the logic sketched in the figure below. These WPs are listed here below:
- WP1: Management,
- WP2: Communication,
- WP3: EBM-DSS: establishing effective management protocols and tools,
- WP4: Development of an Ecosystem-Based ICZM governance protocol in each of the Project target areas,
- WP5: Capacity and competence building,
- WP6: Capitalization of results: the Mediterranean Centre for disseminating EBM tools and methods.
WP1 ensures the coordinated and smooth management of all other MED4EBM WPs. The strategic decision-making and overall project supervision are granted through the MED4EBM Steering Committee (SC), where each Partner is represented. A Project Management Unit (PMU) is also established by the Lead Applicant for guiding and supervising the execution of the project, as well as to handle the official communication with the Managing Authority of the ENI CBC MED Programme. Partners take part in different Work Groups (WG) for the execution of MED4EBM WPs; composition of these WGs varies according to the specific role of Partners in each WP.
MED4EBM core technical activities and outputs are integrated in WP3 and WP4, which establish an Ecosystem-Based ICZM Decision Support System (EB-ICZM-DSS) and Governance Protocol (EB-ICZM-GP) in each of the four MED4EBM target sites across ENI CBC MED Programme Area.
WP5 supports the execution and enhance the effectiveness of WP3 and WP4 by providing ad hoc training packages, mentoring/coaching programs and tools/equipment supplies targeting all relevant EB-ICZM actors and stakeholders of the four MED4EBM focused areas (including MED4EBM Partners).
Technical achievements from WP3, WP4 and WP5 are capitalised in the framework of WP6 through the establishment, in the premises of the Riserve naturali del Lago di Tarsia e della Foce del fiume Crati (managed by AdT), of a permanent Mediterranean Centre for disseminating EBM tools and methods.
A fundamental contribution toward the success of MED4EBM, as well as the effectiveness and sustainability of its outcomes, is given through the execution of a set of communication and awareness activities in the framework of WP2.
As for the partnership roles, UNDP acts as Lead Applicant to guarantee that MED4EBM WPs are effectively and timely deployed. PROGES provides the expertise on the methods to incorporate EBM into ICZM, as well as the PROGES-IS software for establishing the EB-ICZM-DSS (WP3 and WP4). AdT, JREDS, TCNR and INSTM will organize, lead and implement all the activities for the tailor-making of all MED4EBM WPs in their respective target areas, including the liaisons for the active involvement of relevant stakeholders, the definition of context-specific indicators and the related data collection. AdT also establishes the Mediterranean Centre for disseminating EBM tools and methods.
Main Outcomes
An Ecosystem-Based ICZM Decision Support System (EB-ICZM-DSS) is established in each of the four MED4EBM target areas (WP3). To this end, the PROGES Ecosystem Context Analysis methodological protocol is applied which consists of three easy-to-apply sequential steps to handle the complex multi-stakeholder analytical processes that characterize EB-ICZM applications. This protocol adopts simple deterministic ecological assessments, as opposite to the complex statistical and/or algorithmic approaches currently used in ecosystem-based management applications. It identifies and quantitatively assesses the relationships between ecosystem components functions and services, as well as the associated human activities to establish a multi-stakeholders EB-ICZM scheme. The application of this protocol is associated with the use of the PROGES-ISP software for the analysis of spatial and tabular datasets, as well as for the compilation of data-aware advanced reports via a multi-windows interface.
An EB-ICZM Governance Protocol (EB-ICZM-GP) is developed for each of the four MED4EBM target areas (WP4), using the EB-ICZM-DSSs resulting from WP3 to perform a systemic, indicator-based, and participatory analysis. The use of the EB-ICZM-DSSs ensures that: (1) each human activity is managed in the context of all the ways it interacts with marine and coastal ecosystems, and (2) multiple activities are being managed for a common outcome. The backbone of each the EB-ICZM-GPs is jointly drafted by local actors and stakeholders, being their active engagement in the planning and management process the key to the success of EB-ICZM applications. This joint drafting is executed by applying a specific methodology, which identifies in a systematic manner all the significant cause-effect relationships between the different components of the local socio-ecological ICZM dynamics. These cause-effect relationships are then objectively assessed using the EB-ICZM-DSS of WP3 for establishing the said EB-ICZM-GPs to implement flexible management schemes and improve their responsiveness to monitoring results, so as to actually achieve adaptive and effective EB-ICZM.
The above described Outputs of WP3 and WP4 add to the following Output indicators of the ENI CBC MED Programme: 4.4.1.1.a, 4.4.1 .1.b, 4.4.1.1.c, 4.4.1.2.e, 4.4.1.3.f, 4.4.1.5.h.
A Mediterranean Centre for disseminating EBM tools and methods is established (WP6) which operates as a permanent Forum, where regional EBM and ICZM actors are provided with periodic opportunities for exchanging their experiences in applying and updating EBM and ICZM methods and tools. The Forum also acts as a knowledge-sharing platform on EBM tools and methods, benefitting local administrators and stakeholders involved in coastal planning and management, being also a training hub on the innovative EB-ICZM tools and methods promoted by MED4EBM. WP5 also is a parallel contribution to launch the Forum, designing and executing specific activities to involve other Mediterranean EBM and ICZM actors to learn and practice the tools and methods promoted by the MED4EBM.
Institutions, stakeholders, citizens, tourists, are sensitised and their awareness is increased around values associated with ecosystems, thus bringing a lot in terms of biodiversity conservation and sustainable development (WP2). This serving a double purpose:
1. To ensure adequate project’s visibility and build up awareness among various relevant audiences about the principles and practices of EB-ICZM, as well as to disseminate the innovative approaches, methods and tools promoted by MED4EBM;
2. To raise awareness and increase the sense of ownership of local stakeholders and communities about ecosystem, natural, cultural, aesthetic, and spiritual values of their respective areas, and the ensuing need to manage those areas in an integrated and inclusive way.